Biomimicry is an approach to problem-solving and innovation that draws inspiration from nature’s designs, processes, and systems to create sustainable and efficient solutions for human challenges. The term “biomimicry” comes from the Greek words “bios,” meaning life, and “mimesis,” meaning imitation.
Biomimicry involves observing and studying nature’s strategies, such as the way organisms are structured, how they function, and how they interact with their environment, in order to gain insights that can be applied to human technologies, products, and systems. This approach can be applied to a wide range of fields, including engineering, architecture, materials science, medicine, and agriculture, among others.
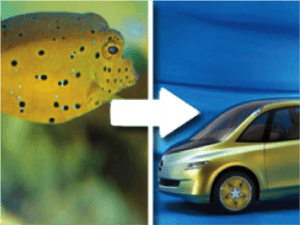
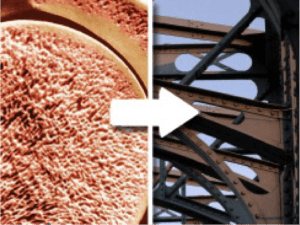
The principles of biomimicry are based on the idea that nature has been evolving and optimizing solutions to complex problems for billions of years, resulting in highly efficient and sustainable designs. By emulating nature’s strategies, biomimicry aims to create innovative and sustainable solutions that are not only efficient, but also regenerative, resilient, and environmentally friendly.
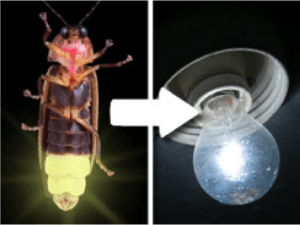
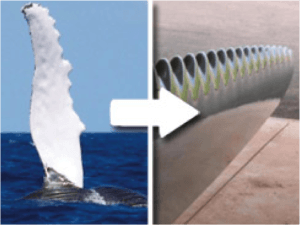
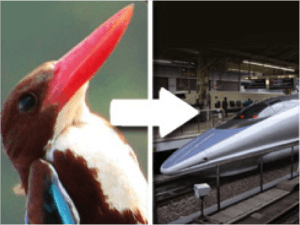
Examples of biomimicry-inspired technologies include Velcro, which was inspired by the hooks and loops of burrs, and efficient wind turbine blades that mimic the design of humpback whale fins. Biomimicry has the potential to revolutionize industries and transform the way humans design and innovate, leading to more sustainable and harmonious solutions that work in harmony with nature.








Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.